Cosmos of the Ancients The Greek Philosophers on Myth and CosmologyParmenides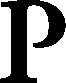 armenides (flourished c. 475 BC) may not have held any strong belief in the gods, certainly not in the anthropomorphic forms Homer and Hesiod had them appear. Instead he made allegorical interpretations of the myths, much like Theagenes had done in the century before, and Empedocles did in his own time.
armenides (flourished c. 475 BC) may not have held any strong belief in the gods, certainly not in the anthropomorphic forms Homer and Hesiod had them appear. Instead he made allegorical interpretations of the myths, much like Theagenes had done in the century before, and Empedocles did in his own time.
Still it was none other than the goddess Dike herself, who declared to him what grand mission he was to engage upon: "It is necessary that you shall learn all things, as well the unshaken heart of well-rounded truth as the opinions of mortals in which there is no true belief." Tradition has it that he was a student of Xenophanes, although not much of their ideas match, and others have said that he was connected to the Pythagoreans, being partly more near his ways of reasoning through mathematical deduction.

They are carried deaf and blind at the same time, amazed, a horde incapable of judgement, by whom to be and not to be are considered the same and yet not the same, for whom the path of all things is backward-turning. The mythology and beliefs of his fellow men must to Parmenides have been a striking evidence of this, since the absurdities of the gods and their doings already before his days had been revealed. This also led him to a firm cosmological view, where what is must always have been, since it cannot have come out of non-being: "Thus it is necessary to exist all in all or not at all." Therefore, when he talked about the ether and the "pure torch of the resplendent sun" coming into being, he must have been referring to a process of change, and not any kind of creatio ex nihilo. This is implied by his saying that the earth, sun and moon, the ether, the stars and the outermost Olympus "strove eagerly to come into being." Just as being and non-being is a pair of opposites, he saw such dynamic counterparts making up the processes of the cosmos — from the pair of Light and Night which equally fill all things, to that of man and woman. But there is a one, not herself the counterpart to anyone or anything, who governs these dynamics: In the middle of these is the goddess who governs all things. For everywhere she is the beginner of union and of painful birth, sending the female to unite with the male and again to the contrary the male with the female. She is also the one to have "devised Eros as the very first of all gods." Where the sun is splendid in the mind of Parmenides, he states about the moon that its light is but a reflection of that of the sun: "Wandering around the earth shining in the night with a borrowed light." About the earth he may have been the first to express the opinion that it is spherical, though not in those actual fragments of his texts remaining.
LiteratureTarán, Leonardo, Parmenides: A Text with Translation, Commentary, and Critical Essays, Princeton 1965.
© Stefan Stenudd 2000

The Greek Philosophers
AristotleIntroductionAristotle's LifeTimelineAristotle's PoeticsAristotle's CosmologyAbout CookiesMy Other WebsitesCREATION MYTHSMyths in general and myths of creation in particular.
TAOISMThe wisdom of Taoism and the Tao Te Ching, its ancient source.
LIFE ENERGYAn encyclopedia of life energy concepts around the world.
QI ENERGY EXERCISESQi (also spelled chi or ki) explained, with exercises to increase it.
I CHINGThe ancient Chinese system of divination and free online reading.
TAROTTarot card meanings in divination and a free online spread.
ASTROLOGYThe complete horoscope chart and how to read it.
MY AMAZON PAGE
MY YOUTUBE AIKIDO
MY YOUTUBE ART
MY FACEBOOK
MY INSTAGRAM
STENUDD PĹ SVENSKA
|
 Cosmos of the Ancients
Cosmos of the Ancients